Zhao Chun1, Jia Jinsheng1, Zheng Cuiying1, Xia Lianqiang2, Wenpeng2
(1 China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, Beijing, 100044,2 Programming and Planning Department of Ministry of Water Conservation, Beijing, 100053)
Abstract: There are more than 87,000 reservoirs in China, of which above 40% are of danger. For the purpose of ensuring the safety and increasing the benefits of dams, the government has proposed a specific project on removal of distresses of 6240 dangerous reservoirs during the three-year period of 2008-2010. This paper gives a brief introduction of the functions of a web-based management system developed by the authors. The technical statistics of distress causes of those dangerous reservoirs are summarized. Correspondingly, some analysis results are also discussed.
Key Words: dangerous reservoirs, web-based management system, distress causes
1 Overview of Dangerous Reservoirs in China
1.1 Reservoirs in China
As the important components of the water conservancy project system in China, reservoirs have played an important role in the national economic and social sustainable development. In the past years, a large number of reservoirs have been built in China to effectively regulate water resources and mitigate the flood and drought disaster. According to statistics, China has built 87,000 reservoirs all types by the end of 2006, of which are more than 500 large reservoirs, more than 3,200 medium-sized reservoirs, and small reservoirs of about 83,300. China is the country with the largest number of reservoirs in the world.
A notable characteristic is that regional distribution of the reservoirs is very uneven. The proportion of reservoirs in the central region of China is 45%, and that in east region is 28%, in west region 27%. There are the most reservoirs in the central region. Seven provinces have more than 5000 reservoirs, and the sum of them exceeds 60% of the total of the country. Hunan has the most reservoirs among all provinces with the number of more than 10,000, which is one-seventh of the total. The Yangtze valley has the most reservoirs among all valleys with the number of more than 40,000.
1.2 Overview of Dangerous Reservoirs in China
Dangerous reservoir we called is the reservoir which main dam has been determined third grade dam according the rules of reservoir dam safety assessment. Third grade dam here is the dam that accords with two conditions: the actual flood standard is lower than the unusual operation flood standard of water conservancy project distresses removal issued by the Ministry of Water Resource, or the dam project is of serious hidden danger and can’t operate normally according to the design.
According to statistics, there are about 37,000 dangerous reservoirs or proportion of 43.7% in those managed by water system, especially the dangerous proportion of small reservoirs is relative high, of which the small (1) type even reached 55.1%.
In distribution, the number of dangerous reservoirs is nearly in direct proportion to the number of its reservoir. So the distribution of dangerous reservoirs is: all over the country but the uneven distribution in each region.
1.3 Main Distress Causes
As a large number of reservoirs built in 1950s to 1970s, some buildings and metal structures have reached the depreciation life after decades running. And because of historical reasons, most reservoirs have a series of problems such as low engineering standards, poor quality construction, aging of serious disrepair, project management backward, supporting facilities shortage, etc. Those cause serious hidden dangers to the safety of reservoirs, and restrict them to take benefit. Generally, distress causes of dangerous reservoirs in China are mainly the following aspects: ① low standard of flood control; ② low seismic standards; ③ poor stability of the dam; ④serious leakage of dam body and foundation; ⑤aging or destroying of water delivery structure, water release structure and the spillway; ⑥metal structures and electromechanical device not to operate normally; ⑦shortage of management facilities and observation equipment; ⑧reservoir sedimentation, landslide, termite damage and so on.
1.4 Dangerous Reservoirs Distresses Removal Project Conducted by China Government
The Chinese Government has always taken great effort into the reservoir safety work which involved people's lives and property safety. For the purpose of ensuring the safety and increasing the benefits of dams, the Government has put on a lot of money and launched an unprecedented scale of the dangerous reservoir reinforcement project since 1998. By the end of 2006, the Government has invested over 20 billion, completed over 1,600 dangerous reservoirs on the reinforcement work. Recently, the government has proposed a specific project on removal of distresses of 6240 dangerous reservoirs during the three-year period of 2007-2009. Because of the large number of dangerous reservoirs, extensive distribution, the complexity of the problem, and limited time, the task is very arduous.
2 Based-on Web Management System Development of Dangerous Reservoirs
The system building mainly includes two parts, one is database construction and the other is front desk management system development.
2.1 Development Goal
According to the entire process information of the dangerous reservoir reinforcement projects which have been carried out, ongoing or planned, establish a Web-based system of dangerous reservoir reinforcement project management system. By the means of data collection, collation, refinement and classification according to user needs, get a comprehensive grasp to the whole view of the reinforcement project, and provide a strong support for planning department for data management, progress tracking, planning schemes, classification summary, statistical analysis, etc.
2.2 Database Construction
Database construction is the foundation for building the system as a whole. The contents of the database construction is: to take the reservoirs reinforcement project invested by the center government as the main management objects, according to management needs, to research E-R, to optimize the structure of data, to edit the data dictionary, to make a logic design, to realize a physical model, to load initial data, and to optimize system performance.
The key step of database design is to design a good set of internal coding for the dangerous reservoir reinforcement project. The coding can not only reflect the basic characteristics of dangerous reservoirs, including their regions, their watershed, the reservoir type, of which series, dangerous type and the investment ratio; but also be benefit for conducive to data query, classification summary, statistical analysis, and other functions.
The content of the database should include:
① The basic situation of dangerous reservoirs;
② Basic conditions of the implementation of the project in the planning;
③ Dangerous reservoirs safety approval and verification;
④ Dangerous reservoir reinforcement project preliminary design review, verification and approval;
⑤ Matching funds commitment of local government and availability;
⑥ Dangerous reservoir reinforcement project investment proposal situation;
⑦ Dangerous reservoir reinforcement project investment approval situation;
⑧ Dangerous reservoir reinforcement project progress in the implementation;
⑨ Dangerous reservoir reinforcement project completion acceptance situation;
⑩ involved in the management of all types of documents and multimedia information.
2.3 Onstage Management System Development
The main task of front desk management system is to provide input, management, maintenance, output interface for the database. By using the system, the task of data management, query, statistical analysis, and remote data submitted can be completed. In the actual development, the system is divided into two subsystems: basic data verification and prophase work report sub-system and investment plans information management subsystem. The network structure of the system is as follows:
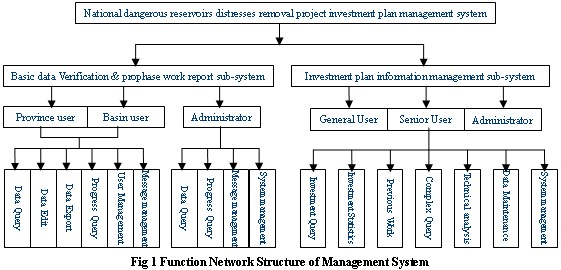
The main function of basic data verification and prophase work report subsystem is just as its name. “Basic data verification” is a function provided to the Province or Basin Users to remotely verify their data of each reservoir’s name, capacity, location, the host basin or so, and correct the mistakes remained in the data. “Prophase work report” is a function provided to the Province or Basin Users to remotely fill in the information of the actual process of dangerous reservoir reinforcement project Prophase work on time, so that timely monitoring and effective tracking can be achieved. The subsystem is deployed in the public Internet, as needed, the system's expected users fall into three categories, namely the maintenance of data users, data verification users, and Back office users. The subsystem supports multi-system collaboration to ensure the accuracy of the data and consistency.
The investment plan information management subsystem mainly carries on the management to dangerous reservoir investment information, with the main functions of data maintenance, data inquiry and statistical analysis. The program modules include “information inquiry”, “investment statistics”, “implementation plan”, “synthesis inquiry”, “technical analysis” five ones. This subsystem is deployed on the local network, as needed, the system expected user also divides into three kinds, for data browsing user (ordinary user), statistical analysis user (high level user), as well as manager user.
2.4 Security Mechanism
As a based-on Web management system, the security design is extremely important. The system namely must cease the illegal visit, also must prevent between the validated user exceeds authority, simultaneously must guarantee the running efficiency and stability. This design follows the rule “The data who own, the data who maintain”. All the pages are completely managed based on the conversation management mechanism. Unauthorized access is forbidden. Users are monitored severely in backstage, and their behaviors of visit and operation are recorded down.
2.5 Main Characteristics of the System
Firstly, B/S architecture is adopted in the system to achieve the distributed application with the users all over the country. It also has the characteristics of easy operation, small amount of maintenance, real-time response and so on.
Secondly, the reinforcement projects are taken as the main management targets, and one-to-one relationship between users and projects are established. The data structure is very clear, so the functions of database management could be achieved easily.
Thirdly, using data dictionary technique to achieve the function of inquiry freely, user could choose the arbitrary columns list needed to display, set the arbitrary filter and sort condition, and get the information they really need.
Fourthly, the query result is shown as a tabular form, with paging, free positioning, jumping between the pages, sorting while clicked on the header line, exchanging with Excel document format, and other practical functions.
Fifthly, the investment data is treated as a data string, and combined with technique of statistical analysis, subtotal and cross-table, the project accounting and investment progress graph could be created timely.
Finally, after the applying of the management system, it has played an important role in the aspects of progress tracing and inspecting effectively of prophase work, also in the information inquiry and investment statistics.
3 Dangerous reservoirs causes disease statistics
The distress causes of dangerous reservoirs could be analyzed from technique by using the database and management system. There are 6,240 dangerous reservoirs in Special Plan, in which main technical information of the location, storage capacity, dam type, dam height, distress feature and reinforcement measures of the whole 1182 large and medium-sized ones have been already collected as a sample database. The preliminary analysis of the distress causes is carried out based on the sample data because of their good representation.
3.1 Analysis of the sample database
3.1.1 Dam Type Category
If classified by construction materials, in the dams of whole 1,182 large and medium-sized reservoirs there are 1059 earth dams, accounting for 89.5 percent, 73 masonry dams, accounting for 6.2 percent, 22 concrete dams, only accounting for 1.9 percent and the rest of 25 cases unknown. It shows that embankment dam is main type in the dangerous reservoirs.
In the 1059 earth dam, there are 628 homogeneous earth dams, accounting for 53.1 percent; 394 core dams, accounting for 33.3 percent; 11 CFRD, accounting for 0.9 percent; 21 of mixed type, 1.8% of the total; 5 of other type, accounting for 0.4 percent.
There are 55 gravity dams and 18 arch dams in the all 73 masonry dams, while there are 10 gravity dams, 7 arch dams, 1 flat dam, 1buttress dam and 2 other type dams in the all 22 concrete dams.
3.1.2 Height distribution
The distribution of the height of the 1182 dams is: there are 445 dams higher than 30m, accounting for 37.6 percent, of which 195 core dams, 135 homogeneous earth dams and 63 masonry dams; 516 dams higher than 15m and lower than 30m, accounting for 43.7 percent, of which 321 homogeneous earth dams and 178 core dams; 190 dams lower than 190, accounting for 16.1 percent, mainly of homogeneous earth dams; dam types of the remain 31 ones are unknown.
3.1.3 Geographical distribution
There are most large and medium-sized dangerous reservoirs in three provinces in the central region, named Hubei (146), Jiangxi (136), Hunan (124). More than a half of the total dangerous reservoirs are located in the six central provinces. Guangxi is the province in the west region of the most dangerous reservoirs, and Shandong is the province in the east region of them.
3.2 Distress Causes
3.2.1 Data Structure of Distress Causes
In order to accomplish the distress causes statistical analysis, an expression like "distress position + distress characteristics" id taken to describe the main distress causes of dangerous reservoirs, and translated to some symbols. Among them, "distress position" is relative to a project position as dam body, foundation, slope, abutment, spillway or tunnel; “distress characteristics” is the common distress summed up by lots of dangerous projects, such as low flood control standard, sliding stability not satisfied, leakage, cracks, deformation, the poor quality of concrete, or termites damage. In further analysis, the extent and the weight factor of distress should be added.
3.2.2 Major categories of the distress causes
According to the dam safety appraisal methods and the report, the distress causes are divided into seven categories:
① Flood control standard categories: Inadequate flood control standards, lack of height, inadequate core height, insufficient capacity of spillway, sedimentation, and so on;
② Project quality categories: Poor quality of construction, uneven soil compaction, high water content, untreated foundation base, broken concrete, unfinished construction projects, termites damage and other hazards;
③ Structural safety categories: Inadequate dam stability factor of sliding resistance, slope instability, weak dam, inadequate cross-section, the dam foundation cracks, large deformation, uneven settlement, the tensile stress exceeding norms; cracks, fracture, exposed tendons, peeling, erosion, seepage found in the deliver buildings and spillway building; dam foot damaged by washing out;
④ Seepage safety categories: Foundation of the dam leakage, seepage around the dam, contact erosion, scattered soaking, swamping, mass flow, piping, abnormal uplift pressure, infiltration destroy, unsafe seepage and stability;
⑤ Seismic Safety categories: Seismic safety unsatisfied according hydraulic seismic criterion, soil liquefaction;
⑥ Metal structure safety categories: Aging, corrosion, leaks, and damage of metal structure and mechanical-electrical equipment, out of control;
⑦Operation and Management categories: Lack of management facilities, observation facilities, and flood prevention equipment.
3.2.3 Main Distress Feature Refinement
Based on the refinement of 1,182 dangerous reservoirs distress features, mainly used the distress features of dam body, we raised 15 major characteristics of the distress, as the basis of statistical analysis of data. Characteristics of the distresses are: flood control standard, the quality of engineering structure, the foundation cracks in the dam, the dam deformation and settlement, the slope stability, leakage in foundation and dam, seepage safety and stability, seismic safety, earthquake liquefaction, damage in water delivery & release buildings, damaged spillway buildings, damage in metal structure, termite hazards, sedimentation, management and observation facilities.
3.3 Statistical analysis of Distress Causes
Take the information of 1,182 large and medium-sized dangerous reservoirs as a sample database, by using Statistical analysis method to study the main distress causes of all the reservoirs, earth dam, masonry dam, concrete dam, homogeneous earth dam, the core dams, respectively. Some of the results are listed as follows:
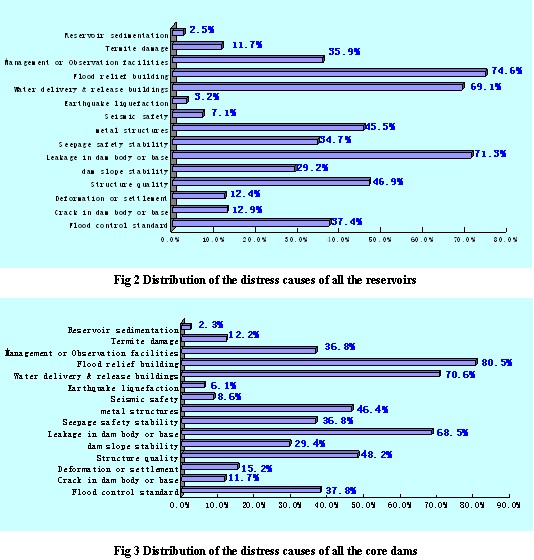
In all of the reservoirs, the ratio distribution of the characteristics of various distresses is shown in Fig 2. Flood relief building broken is the cause of the largest ratio, reaching 74.6 percent, followed by ratio of leakage of the dam foundation, accounted for 71.3 percent; the ratio of water delivery & release buildings has reached 69.1 percent, while the ratio of low flood control standards only 37.4 percent.
In the 394 core dams, the ratio distribution of the characteristics is shown in Fig 3. Flood relief building broken is still of the largest ratio, reaching 80.5 percent; the ratio of water delivery & release buildings has reached 70.6 percent, the ratio of leakage of the dam foundation dropped a little to 68.5 percent. It indicates that core dam could reduce leakage problem to a certain extent compared to the average level.
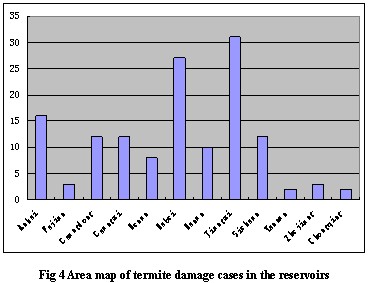
Choose the regional distribution of termites damage of 138 cases to make a special analysis, the result is shown in Fig 4. It shows that the termites hazard of the reservoirs mainly occur in 13 provinces, and concentrate in the central region. The sum of top three numbers of the cases in each province accounts for about half of the total.
4 Summary
At the beginning, basic situation of dangerous reservoirs in China is described in this paper, then a brief introduction to the functions and development of Web-based management system of dangerous reservoirs. Using the database and management system, statistics analysis of distress causes of 1182 large and medium-sized reservoirs of dangerous is made. The results show that: Flood relief buildings damage and leakage of the foundation and dam are exactly the main two reasons to make reservoirs dangerous.
References:
[1] Special Plan of Dangerous Reservoirs Reinforcement (R) Ministry of Water Resources, State Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Finance 2008.4.
[2] Ru Naihua, Niu Yun-kwong. Dam Incidents and Safety • Earth dam (M). China Water Conservancy and Hydropower Press, 1997.2.
[3] Zou Hua, Servlet & JSP Programming Technology and Examples (M) Posts and Telecommunications News Press, 2001.10.



